This move left China with a lopsided economy, especially its state-owned sector, and has added a unique regional dimension to the restructuring that would anyway be occurring to state-run industries going through the sort of changes that China has been experiencing since Deng Xiaoping set off down the path of economic reform in the late 1970s.
Though it might cause Mao to turn in his grave, private enterprise now accounts for the majority of economic output in China. It is more efficient and faster-growing than the state sector. It is not constrained by being an anchor industrial employer in places where it often has no natural advantages.
Private companies in China remain small--agriculture, wholesale and retail distribution and construction are dominated by thousands of small family firms--and they face considerable barriers to growth; access to markets and capital still depends greatly on connections. They are, though, on the whole profitable.
The state sector, composed of about 150,000 state-owned enterprises, is a different story. These firms are often big and unprofitable. An study by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) based on data from 2003 found that they wrung half the productivity from twice the capital.
State enterprise assets represent about 85% of China's gross domestic product, about three times higher than in even the most state-dominated Western European economies, France and Italy, and well above the rate typical in economies making the transition from developing to developed.
Not all are hopeless basket cases. Productivity and profitability are improving surely, if slowly. The return on equity at state industrial firms rose from 3.4% in 1998 to 10.2% in 2003, according to the OECD study. That is short of the private sector's 14.4%, but still passable.
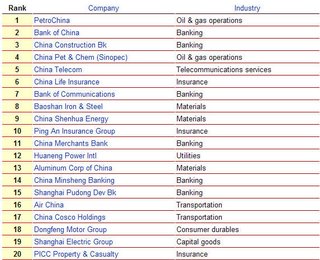
However, the best performance is concentrated in the largest 20% or so of state enterprises. They tend to be the ones that Beijing is using to drive development across the economy in the industries that are the boiler rooms of growth: energy ( PetroChina), banking ( Bank of China), utilities ( Huaneng Power), chemicals ( Sinopec), heavy industry ( Baoshan Iron & Steel), telecommunications ( China Telecom) and transport ( Air China).
Beijing's industrial policy for its state-owned enterprises is two-pronged: to develop national champions that can compete in world markets, and to ease the strain the basket cases impose on the national treasury.
Except at the top end (the companies that make our list of China's largest companies), even China's biggest companies are not so sizable by world standards. Only 14 make the list of the world's 500 largest companies by sales, of which eight are state-owned.
Hence, a policy emphasis on achieving economies of scale and scope. Since the late 1980s, informal links between large enterprises have been formalized through merger and consolidation. That has distilled 120 industrial groups identified as national A-list companies, with a further 2,300 similarly preferred companies at provincial and city levels.
The national champions have been given more decision-making and financial autonomy and priority in the allocation of state-controlled resources, including investment and capital.
They have been encouraged to create research centers (even China's biggest companies devote only 1% of sales to research and development, on average--compared to 5% in the West) and develop their foreign trade. They have also been earmarked for stock-market listings.
They were initially given protective tariff support, although that is being removed in line with China's World Trade Organization entry obligations.
Beijing is also trying to pull off a delicate balancing act: imposing the disciplines of the market on management while keeping policy control of its national and local champions firmly in trusted hands. This has led to the creation of a hybrid group structure, not dissimilar to the industrial groupings that underpinned Japan Inc.
Under this model, a holding company, run by politically appointed managers, controls a network of associated operating companies via controlling or minority shareholdings. One or more of the associated companies may be selected as the vehicle for a public listing on a stock exchange; others of the associated companies may be designated to absorb a large amount of the group's underperforming assets.
A side benefit of this structure is that it has created national industrial networks that circumvent the local protectionism and vested interests that are a legacy of Mao's industrial policy. That, in turn, has eased Beijing's way toward meeting its WTO market-opening obligations.
Since 2003, supervision of the very largest state-owned companies in China has fallen to the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC), a high-level commission whose writ runs to about 180 companies. It has set an internal target of having 50 Chinese companies, including state-owned ones, among the largest 500 companies by sales in the world by 2015.
To this end, it recently linked the salaries and bonuses of the presidents of 30 of the biggest state-owned enterprises, including China National Offshore Oil, to the profitability of their companies.
More M&A can be expected in the state sector as China seeks to create more big companies that can compete internationally. Yet perversely, Beijing will try to do this while tightening its hold on the sector rather than loosening it.